Introduction
To boost business effectiveness and efficiency in IT infrastructure, many companies seek solutions that provide them a better way to manage their valuable data and processes. The term “cloud computing” has become popular today due to the ultimate advantages that it could bring to business –flexibility of managing computers and infrastructure anywhere with an Internet connection. So what is “cloud computing”? What are types of service that cloud computing offers? What are the benefits of cloud computing?
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the concept of using a group/network of servers hosted by a third-party company to provide a remote (virtual) infrastructure for users and organizations through the Internet. In addition, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cloud computing as “…a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g. networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.” Cloud computing technology provides both computing power and a collaboration environment for businesses and organizations to run, compute, and store their data as well as a collaborative environment in which to work.
Technology Overview
Types of services
Cloud computing offers three (3) main types of service: SaaS (Software as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service). Each type of service focuses on a unique set of needs and requirements.
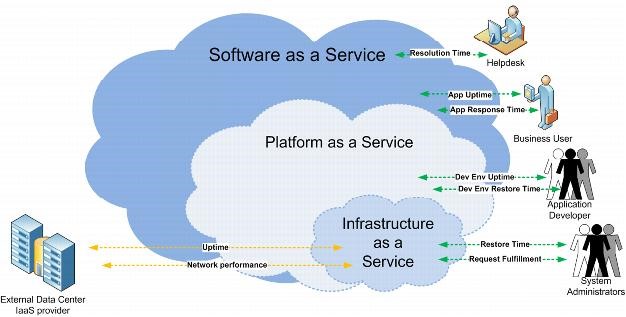
Source: vmware.com
Figure 1: Cloud computing layers
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Salesforce.com defines Software as a Service (SaaS) as a way of delivering an application over the Internet as a service. Instead of installing the software on a locally hosted server, the software will be installed on third-party infrastructure and streamed to users and organizations as a service. This streaming process is called “on-demand usage.” SaaS has been widely used by many companies and organizations to reduce cost and improve efficiency because the software is only used as needed. Moreover, the ability for each user to customize applications to fit their needs is a feature of some SaaS providers. As companies and organizations use SaaS within their environments, they can modify the application to run and perform specific tasks to boost business outcomes.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is, “…the ability to provide customers storage, networks, and other fundamental resources to deploy and run arbitrary software such as operating systems and applications via the Internet.” Customers do not manage the infrastructure in the traditional sense of dealing with memory, hard disks, configuration, maintenance, or upgrades. All of these hardware components are provided by a third party company hosting the IaaS. As businesses perform transactions using cloud-computing service, IaaS offers database, servers, and network clusters that connect all the power from every single entity within the infrastructure to achieve the best performance.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
As Salesforce.com points out, “Platform as a Service — or PaaS — is a proven model for running applications without the hassle of maintaining the hardware and software infrastructure at your company.” PaaS is a cloud computing model that provides applications over the Internet. The cloud provider (third party company) delivers both hardware and software tools, so the customers do not need to host or install any software on their end. With PaaS, businesses use the entire platform to perform transactions and processes without the hassles of hosting the infrastructure or maintaining any software. Everything is ready and being delivered through the Internet.
Types of cloud – deployment models
There are four (4) types of cloud – deployment models. Each type has advantages and disadvantages; each type and could be used for different purposes. The four deployment models are private cloud, community cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Private Cloud
Private cloud is hosted for exclusive use by a single organization/company. It may be owned, managed and operated by that organization or company. However, the private cloud is located in a remote location and is accessed via the Internet. This is one of the most popular deployment models that companies are using today due to its privacy and security. Examples include , Office 365, Google Apps..etc.
Community Cloud
A community cloud is similar to the private cloud but more targeted to a specific community of consumers from an organization or company. This type of cloud is great for team collaboration or cross-organization data sharing. Examples include Github, Cloud9, SoundCloud…etc.
Public Cloud
Public cloud, as its name indicates, is the cloud infrastructure that is open for public use. This cloud can be used by anyone with no restrictions. This type of cloud is very useful for public data sharing that all companies and organizations are sharing data with the public.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is a mixture of two (2) or more types of deployment models previously discussed. Hybrid cloud could be used in many scenarios when companies and organizations want to collaborate on a common or shared business matter and want to open up their private cloud for a specific purpose.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Everything has advantages and disadvantages; so does cloud computing. There are a couple of advantages that cloud computing provides businesses and organizations to improve effectiveness and efficiency significantly. First, because cloud computing runs online and is managed by companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, IBM or HP, businesses do not need to pay for infrastructure hardware, software and technical resources. They only pay for what they use. Therefore, IT overhead costs can be reduced significantly. Also, cloud resources can be expanded easily by a couple of mouse clicks. There are no limits to resource usage as long as the company can pay for what they use. Moreover, security of the data in the cloud is managed by large corporations that can dedicate extra resources to security that many businesses simply cannot. This may add an extra layer of protection for sensitive data and information. Lastly, the central collaboration environment provided by cloud computing is excellent. When all services are integrated seamlessly, data and information may be integrated with multiple platforms: software, physical locations, and people. For example, documents could be sent and edited live in Microsoft Office 365 or Google Apps environment. In this perspective, cloud computing creates a new definition of modern collaboration where people from different locations work together effectively.
Cloud computing does have some disadvantages. The first disadvantage is Internet connection dependency. Without an Internet connection, companies and businesses can not access their cloud environment. Also, the connection must be fast enough to transmit all data and commands to the cloud environment. A slow connection could cause data corruption and lost. Second, because a third party company is managing the environment, it puts companies and organizations at risk if that host goes out of business. Lastly, if hackers access the cloud infrastructure, it will be extremely hard to stop them instantly because there is no easy way to shut down the infrastructure immediately.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become more popular than ever. In the future, traditional infrastructure setup could be completely replaced by this new technology. The cloud computing market is booming as many businesses and organizations want to reduce their IT infrastructure overhead. As more companies are joining this revolution, it is critical for modern businesses to understand the concept and utilize it successfully. The future of computing is finally here, and it is maturing every day. However, it is up to the business to use it wisely and effectively.
References
- NIST Cloud Document. (n.d.). Retrieved May 5, 2015, from http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-145/SP800-145.pdf
- What is Cloud Computing Technology? – Salesforce.com. (n.d.). Retrieved May 5, 2015, from http://www.salesforce.com/cloudcomputing/